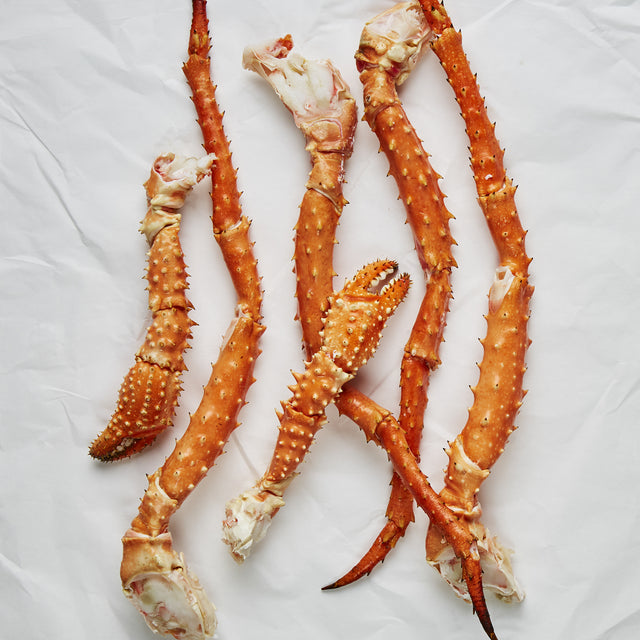
Everything you’ve ever wanted to know about Alaska King Crab, rounded up and all in one place. Happy learning!
Number of king crab species: Around 18 species of king crab are known to exist in Alaska waters. Four of those king crab species are fished for.
Food that king crabs live on: Baby king crab eat phytoplankton and zooplankton. Juvenile king crab eat diatoms, protozoa, hydroids, other crab, and other organisms that live on the ocean floor. And finally, adult king crab eat worms, clams, mussels, snails, brittle stars, sea stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, barnacles, fish parts, and algae.
Depth and distance from shore: Golden king crabs live up to 1,600 feet deep in waters off Alaska and Russia. Red and blue king crabs instead like the sandy bottoms of shallower water, around 200 feet. The furthest point for king crab fishing is 200 miles from shore.
Can I get my king crab live? Probably not. Historically, live king crab has only gone to nearby Asian communities, due to the shipping time. However, due to lower prices of king crab and requests from leading US chefs for live king crab, major metropolitans are starting to carry live king crab flown in by air.
Spawning season: The spawning, or breeding, season generally begins in January and continues through June. King crab will typically spawn in water less than 150 feet.
Biomass: The technical term for the estimated amount of king crab in the ocean. This is an important number for determining how much king crab is permitted to be fished commercially each year.
Landings: Fishermen and others use the term landings to track the amount of king crab caught and brought to land for distribution.
Alaskan coastline: The longest general coastline of any state, measuring 6,640 miles.
Alaskan industries and employment: Fishing is the leading economic activity in many parts of Alaska. As of 2004, Alaska had 14,000 workers employed in the agriculture, forestry and fishing industries which translates into 1% of Alaska GDP.

The Bering Sea: Over 50% of frozen fish consumed in the US comes from the Bering Sea, one of the largest marine ecosystems in the world. In the last half century, there have been two shifts in the climate and ecosystem of the Bering Sea. The significant transition from arctic to sub-arctic conditions (temperatures above freezing) caused less sea ice, which in turn created increased levels of solar energy in the ocean. The rise in ocean temperatures negatively affected the biomass of bottom species, which in the early 80s resulted in significant drops in king crab production.
Dutch Harbor, Alaska: The main port of call for king crab fisherman. The majority of king crab fishing boats leave each season from Dutch Harbor and return after the season for processing and shipment. (See a live webcam of Dutch Harbor). Most observer assignments begin at Dutch Harbor in which state officials keep track of king crab fishing on vessels.
*Photos courtesy of Alaska Seafood